Specialist Exams
TOPOGRAPHICAL ABERROMETRY
The aberrations are the deformations of the light signal (wavefront) that this undergoes when crossing the cornea, the lens, the aqueous humor, the vitreous body before reaching the retina. Even hyperopia, astigmatism and myopia represent ocular aberrations (low order). Corneal aberrometry is a diagnostic test that allows you to check for any changes in the anterior corneal surface and is used for a pre-operative evaluation of corneal refractive surgery or for an evaluation of the refractive result after refractive surgery. For the greater precision of the result of this diagnostic test it is advisable to suspend the contact lenses 3-4 days before, if you use soft contact lenses and at least 2 weeks earlier if using gas permeable or semi rigid lenses. It is a computerized exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
ARGON LASER
 it is used in ophthalmology to treat diseased areas of the retina (as in diabetic retinopathy or in vascular occlusions of the retina) or in other cases to "weld" the retina around lesions that could lead to a detachment of the retina (treatment for retinal holes, lacerazioni retiniche, or rhegmatogenous degenerations of the retinal periphery). With its thermal action, the argon laser produces a "photocoagulation” (to all intents and purposes a "burn") of the retina with the advantage of drying and avoiding the formation of new vessels in diabetic retinopathy and vascular occlusions and a tenacious adhesion such as "barrage"In the lacerations, in holes and peripheral degeneration. However, it is a non-invasive treatment, (drops for pupillary dilation and a few drops of anesthetic are instilled to place a specific lens on the eye). The duration varies according to the type of lesion to be treated (but it is usually a few minutes) at the end the patient can resume his own activities but it is advisable to have an accompanying person present.
it is used in ophthalmology to treat diseased areas of the retina (as in diabetic retinopathy or in vascular occlusions of the retina) or in other cases to "weld" the retina around lesions that could lead to a detachment of the retina (treatment for retinal holes, lacerazioni retiniche, or rhegmatogenous degenerations of the retinal periphery). With its thermal action, the argon laser produces a "photocoagulation” (to all intents and purposes a "burn") of the retina with the advantage of drying and avoiding the formation of new vessels in diabetic retinopathy and vascular occlusions and a tenacious adhesion such as "barrage"In the lacerations, in holes and peripheral degeneration. However, it is a non-invasive treatment, (drops for pupillary dilation and a few drops of anesthetic are instilled to place a specific lens on the eye). The duration varies according to the type of lesion to be treated (but it is usually a few minutes) at the end the patient can resume his own activities but it is advisable to have an accompanying person present.
AUTOCHERATOMETRIA
Autokeratometry is an instrumental examination which consists of measurement of the external curvature of the cornea in order to identify any refractive errors of the eye, as in the case of astigmatism and is performed using an instrument called an autokeratometer, computerized today (while keratometry or ophthalmometry, used Javal's keratometer- Schiòtz). It is a useful exam, along with the topography, in the diagnosis of the Keratoconus, a rare corneal disease, but at times strongly disabling the visual function. As mentioned it is a computerized exam, non-invasive, no drops are instilled and lasts a few seconds and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
AUTOREFRACTOMETRY
Auto-refractometry is a computerized diagnostic test capable of determining the objective evaluation sight defects, like myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. The test performed by the auto refractometer, he is able, in a few seconds and in a non-invasive way, to identify the refractive defect of the eye subjected to the examination with absolute precision. The easy-to-perform exam, non-invasive, for both adults and children, it is carried out with high precision computerized tools. For children from 0 a 6 age, in our studio, an auto refractometer is used which allows for the acquisition of any visual defects at a distance of over 1 metro, instrument specially designed and built for these little patients. It is a computerized exam, non-invasive, no drops are instilled and it lasts a few seconds. At the end of the evaluation, the patient can resume his activities without particular precautions or warnings.
BIOMETRY
Biometrics is a diagnostic test of the eye that is capable, in a few seconds and in a non-invasive way, to measure very precisely both its anteroposterior length and other structures of the eyeball. Biometrics can be ultrasound and optical. Ultrasound biometry is performed through the use of an ultrasound probe (A scan), while optical biometrics, more recent introduction into clinical practice, is based on partial coherence optical interferometry and uses a light beam. Both can be used for the calculation of the artificial lens which is then implanted in the cataract surgery and these methods can be used in our study. A recent use of optical biometrics, is that of the study of the progression of myopia in children and adolescents capable of determining the increase in the anteroposterior length of the eyeball regardless of the accommodative phenomena (Myah Topcon. Link https://topconmyah.com/) and therefore to prescribe the latest generation lenses that allow, not just the correction of myopia, but which represent a "treatment" aimed at slowing the progression of myopia in this age group of young patients.
They are computerized exams, non-invasive lasting a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings. Ultrasound biometry involves the instillation of anesthetic drops.
BUT (acronimo Break Up Time)
It is a test for the evaluation of tear function which, combined with other tests, helps us in the diagnosis ofDry eye. Proposed by Norn in 1969, it is expressed in the time in seconds that elapses between a blink and the formation of the first "dry spot" (dark area), in the precorneal film, indicator of the stability of the tear film. A GOAL value ≥ 10 sec is normal. A value GOAL ≤ 10 sec is pathological and indicates dry eye. The Non Invasive Tear Break Up-Time (NIBUT) It is the time that elapses between a blink and the formation of deformations in a pattern reflected on the cornea. Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out this test and computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks. They are computerized exams, non-invasive lasting a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
COMPUTERIZED FIELD OF VIEW
The visual field is the whole portion of space seen by the eye when it fixes a defined point in front of it. Then the examination of the visual field, allows you to study the integrity of the optical pathways from the eye to the occipital cortex where they carry the visual information. It is therefore a fundamental exam for the study of diseases such as glaucoma, for some pathologies involving the central or peripheral retina, in disorders and diseases related to the optic nerve and cerebral optic pathways and also in eyelid ptosis. It is a computerized exam, non-invasive, no drops are instilled and of an average duration of 20-30 minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE CURVE FOR GLAUCOMA
The intraocular pressure is not constant throughout the day and increases in pressure can be detected that can escape a single measurement. In such cases it may be necessary, through tonometry, check the intraocular pressure several times throughout the day and then draw a daily curve that allows us to have more accuracy in the evolution of ocular hypertension towards glaucoma.
ULTRASOUND OF' IRIDO-CORNEAL ANGLE OF THE ANTERIOR SEGMENT (UBM)
Ocular ultrasound of the anterior segment uses ultrasound to visualize the internal structures of the eye. Ultrasounds bounce off the tissues, generating “tomorrow” which are collected and processed to form diagnostic images. The Ultra Bio Microscopy (UBM) highlights structures of the anterior segment of the eye otherwise not viewable, in particular, it allows you to view the width of the corneal iris angle and the ciliary body. For this reason it is indicated in the control of narrow-angle glaucoma and in the assessment of the risk of occlusion of the corneal iris angle and consequent acute glaucoma. It’ also useful for the study of corneal pathologies, of the iris and the iridocorneal angle. Also important in evaluating the success of numerous surgeries. The exam is not invasive and does not require any preparation: after administering an anesthetic eye drops, a silicone cup filled with physiological solution is placed between the eyelids in which the probe connected to the ultrasound is immersed.
EYE ULTRASOUND
Ocular ultrasound of the anterior segment uses ultrasound to visualize the internal structures of the eye. Ultrasounds bounce off the tissues, generating “tomorrow” which are collected and processed to form diagnostic images. Ocular ultrasound is most useful when there are opacities of the optical media that prevent a visualization of the fundus: an advanced cataract or for example a haemorrhage in the vitreous. Orbital ultrasound allows you to study the lacrimal gland, the oculomotor muscles, the optic nerve and other structures of the orbit. The exam is not invasive and does not require any preparation: after administering an anesthetic eye drops, gel is placed on the closed eyelid and the ultrasound probe or drops of anesthetic are placed on the eye muscles.
EXAMINATION OF THE TEAR FILM
Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out this test and computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks. It is an exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
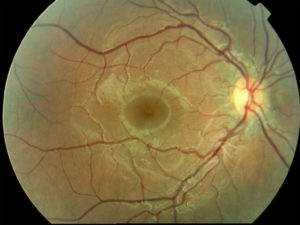
EXAMINATION OF THE OCULAR FUND
Fundus examination (o del farm of the eye), is a diagnostic eye exam through which the ophthalmologist studies the internal structures of the eye: the vitreous body, the retina (both in the central area, this macula, due to the possible presence of macular degeneration or other macular affections, both the periphery, anatomical area from which a retinal detachment may originate due to the presence of degenerative areas located here), the optic nerve and it state of the retinal circulation, both arterial and venous (the ophthalmologist is the only doctor able to see the "state" of the vessels of the human body). It is a non-invasive examination and requires pupil dilation (the duration of which, except in special cases, it's about 1-2 hours) and can be performed with various more or less sophisticated instruments for a better and in-depth exploration of the internal structures of the eye. At the end of the evaluation, the patient can resume his activities without particular precautions or warnings.
ESAME OF THE VISUS
Theesme of the visus or acuity measurement visual it is the examination through which ophthalmologists are able to assess the actual visual capacity of the patient's eyes. It is done by asking the patient, examining one eye at a time, to read the letters projected on a table (this ottotipo) or viewed on a particular computer, which gradually present a decreasing size whose lines correspond to "tenths of sight" (the prime riga equals 1/10 and so on; if the patient reads 3 lines will have 3/10, if he reads 10 lines will have 10/10 of sight). During this measurement, the ophthalmologist is also able to evaluate the "Best optical correction" for that particular eye (which he will then write in the prescription of eyeglass lenses) which allows you to read the 10/10 or what that eye can read. Many patients confuse the "tenths", which represent the lines that the eye can read with or without glasses with "Diopters" which they represent instead the measure of the power of the lenses which when placed before the eye allow you to read the "tenths". They are computerized exams, non-invasive lasting a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings. For the greater precision of the result of this examination and for a correct prescription of the glasses (and / or contact lenses) it is advisable to suspend the use of contact lenses 3-4 days before, if you use soft contact lenses and at least 2 weeks earlier if using gas permeable or semi rigid lenses. In our study the evaluation of the best optical correction, it can be done using a computerized tool (foroptero), and it is in any case a non-invasive examination, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
CONTRAST SENSITIVITY TEST
The bright contrast is the ability to perceive the slightest difference in brightness (hue) between two adjacent surfaces of the same color, representing in its maximum scale that phenomenon that allows us, for example, the distinction of print characters on a white sheet. This sensitivity is very high, but it gets worse in some eye diseases involving the retina, the optic nerve and in some diseases, such as diabetes, he glaucoma, as a result of refractive surgery, in taking some medications, it also varies with age and is influenced by visual acuity, the quality of the optical correction worn (contact lenses or glasses), the diameter of the pupil, the presence of corneal opacities or the presence of a cataract. The measurement is carried out using an optotype with the LCD screen where lines formed by letters of the same size are displayed, of the same color but of a different shade, which is reduced more and more until the subject can no longer distinguish the letters. The exam as well as for the study of the aforementioned diseases is required for the issue of a driving license or in some sports. It is a computerized exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
ORTHOPTIC EXAMINATION
The orthoptist (or assistant in ophthalmology) is the professional figure who supports the ophthalmologist, in prevention, in the assessment and visual rehabilitation of motor and sensory disturbances of vision. So with the visit orthoptic, the orthoptist is not only able to assess the possible presence of an alteration in the neuromuscular system of the eyes (strabismus, abolition, diplopia, exophoria, esoforia, convergence deficit, etc..), but also to treat these diseases in synergy with the ophthalmologist and often, in small patients, with parents, in order to recover the correct neuro-functional balance of ocular motility and visual function. It is also useful in the study of patients who are candidates for refractive surgery and those with a high refractive defect in cataract surgery. The orthoptic examination is an examination, non-invasive, drops are not instilled is lasting 20-30 minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
EXOPHALMOMETRY
Exophthalmometry is the examination that allows the ophthalmologist to evaluate the protrusion of the eyeballs by referring to the bony edge of the temporal orbit. It is carried out by leaning on a graduated ruler (Hertel's exophthalmolmeter) on the outer edge of the orbit of both eyes and through a system of mirrors, it is possible to measure the distance in millimeters of the cornea vertex from the orbital edge. Such values, in physiological conditions, vary in relation to the shape of the orbit and the length of the eyeball, but normal values are considered to be those between i 10 ed i 16 mm, in women and children and between 14 ed i 20 mm in men. In pathological conditions, come in Graves' disease (hyperthyroidism) due to thickening of the eye muscles or the presence of lesions that occupy space within the orbit, as a cyst, angiomas, tumors or aneurysms, these values can exceed 28-30 mm. It is an exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
HD PHOTO OF THE FRONT SEGMENT
The photograph of the anterior segment of the eye allows you to document and monitor the growth of pathologies affecting the eyelids (in, warts, tumors, ectropion entropion ecc), conjunctiva (papillomas, cyst), of the sclera and cornea (fat, pterygium, scars), of the pupil and iris (in, neoformations), of the corneal iris angle and of the lens. The examination is carried out using the slit lamp and in our office it is possible to have a documentary HD resolution of the aforementioned pathologies. It is an exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
PHOTO OF THE REAR SEGMENT
Fundus photography allows us to document pathologies affecting the macula, retinal, of the optic nerve and the circulation of the retinal vessels (venous thrombosis, arterial occlusion), as for example in diabetes, in arterial hypertension, etc.. It is very important to document the macular area (related macular degeneration) and the study of optic nerve fibers. It is an exam, non-invasive, pupil dilation drops are instilled, it lasts a few minutes and at the end of the evaluation the patient can resume his activities without particular precautions or warnings.
GONIOSCOPIA
Gonioscopy is a diagnostic method used by the ophthalmologist to explore the irido-corneal angle (that is, the anatomical angle that is formed between the cornea and the iris). The purpose of this investigation is to evaluate above all whether the iridocorneal angle is open or narrow, thus allowing the diagnosis of narrow angle glaucoma o highlighting pathologies of this small hidden region of the eye (in, sinechie, etc..). The examination is carried out under the slit lamp using a lens equipped with a 62 ° tilted mirror (Lente di Goldmann), which is placed on the cornea after instillation of anesthetic drops and the application of a layer of methylcellulose. It is an exam, non-invasive lasting a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
IRIDECTOMIA YAG LASER
The iridocorneal angle (that is, the anatomical angle that is formed between the cornea and the iris), contains the "trabeculate", which is the filter through which the water produced leaves the eye. The angle can be examined with a method called "gonioscopy”. (see). In particular predisposed eyes, as in small bulbs or with high hyperopia, with pupillary dilation, the angle can suddenly close causing a sudden increase in eye pressure, which can cause irreversible damage to the optic nerve and possible loss of vision (acute attack of narrow-angle glaucoma). L’iridotomia yag laser is the treatment of choice in angle-closure glaucoma and in the eyes at risk for this condition: those who have a closed angle for at least half of the eye and high ocular pressure (narrow angle glaucoma) and those who have a closed angle but normal eye pressure and no optic nerve damage, as a preventive treatment. The laser yag iridotomy in these eyes creates a "hole" at the periphery of the iris, thus avoiding that the corner can close and the eye pressure increase. Drops are instilled in the eye half an hour before treatment, making the pupil smaller (miotics). They are then instilled, a few drops of anesthetic to place a specific lens on the cornea with methylcellulose to perform the laser treatment. The procedure usually takes 5-10 minutes and the patient may in some cases feel a slight pain lasting a few seconds.
OCT (tomography of the macular region, optic nerve and nerve fibers)
L'OCT (from the Anglo-Saxon acronym of Optical Coherence Tomography or optical coherence tomography) is a recent non-invasive diagnostic technique that allows, without coming into contact with the eye, to obtain through a series of photographs taken using the reflection of the laser and infrared rays sent on the retina, "in vivo" images of the retina itself (with precision, depending on the tools, which reaches up to 5 micron) which you subsequently process by your computer, make visible, in "tomographic" sections, the smallest details of the retinal area examined. The analysis of these images allows to highlight all the pathological conditions affecting the anterior segment (OCT of the anterior segment) and the posterior pole of the patient. Therefore, OCT is useful in the diagnosis of degenerative retinal diseases (age-related macular degeneration etc. ), in macular puckers (in interface syndromes), in the macular holes, in vascular forms (thrombosis, etc), in diabetic retinopathy (diabetic macular edema, ecc), in the central serous choroiditis, in tumor forms, but also in the post-surgical control of patients undergoing retinal detachment or other retinal diseases. The OCT also allows the study of the optic disc, ganglion cell, of the layer of nerve fibers that make up the optic nerve, representing the essential examination even if it is complementary, along with the field of view, to pachymetry and tonometry, in the preventive evaluation and monitoring of glaucomatous disease. OCT is the essential examination in the diagnosis and assessment of the course of age-related macular degeneration as well as in the prescription and timing of intravitreal therapy for the evolution of this disease The examination also allows you to assess what visual recovery a patient may have about to undergo cataract surgery or retinal surgery. As mentioned, it is a non-invasive examination, lasting a few minutes which can also be performed without pupil dilation and the patient at the end of the assessment can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
THE OCT OF THE ANTERIOR SEGMENT.
L'OCT (from the Anglo-Saxon acronym of Optical Coherence Tomography or optical coherence tomography) is a recent non-invasive diagnostic technique that allows, without coming into contact with the eye, to obtain through a series of photographs taken using the reflection of the laser and infrared rays sent on the anterior segment of the eye to obtain high-resolution images of the cornea, of the anterior chamber, of the iris, of the iridocorneal angle, of the pupil and lens. It is of fundamental importance in the prediction and post-operative course of some types of refractive surgery and in the diagnosis and therapy of some diseases of this eye region. As mentioned, it is a non-invasive examination, lasting a few minutes that does not require pupil dilation and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
PACHIMETRIA (ultrasound and optical ultrasound)
Pachymetry is a diagnostic test by which accurate measurement of the thickness of the cornea is obtained, i.e. the transparent dome in front of the iris (the colored part of the eye). The cornea in normal conditions in the center is about thick 540 micron, that is, thousandths of a millimeter (0,54 mm) and the thickness increases in the area near the center (about 550 micron) and in the peripheral (650 micron). In the presence of some diseases, the cornea may be thicker or thinner. The measurement of the thickness of the cornea can be performed with an ultrasound probe (ultrasonic pachymetry), by infrared radiation (optical pachymetry) or through OCT (of the anterior segment). All three methods can be performed in our office. The pachymetry represents the exam fundamental in refractive surgery procedures affecting the cornea, often conditioning (together with pupillometry and refractive defect) the choice of the type of intervention. Finally, it is indispensable as a corrective factor in the evaluation of ocular pressure measurement in ocular hypertension and glaucoma. It is a non-invasive examination, lasting a few minutes that does not require pupil dilation (only in ultrasonic pachymetry a few drops of local anesthetic are needed) and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings
STATIC AND DYNAMIC PUPILLOMETRY
It is an exam through which pupil diameter is measured both in strong light conditions (fotopica) than low lighting (scotopica). The information collected through this examination is used by the ophthalmologist both for the study of refractive surgery and in modern cataract surgery, because the pupillary kinetics significantly affects the quality of the image produced on the retina. It is a non-invasive examination, lasting a few minutes that does not require pupil dilation and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings
SYNOCTOPHORUS
The synoptophore is an ophthalmological instrument considered the "gold standard" for the diagnosis and corrective therapy of the various dysfunctions of ocular motility, like squint, Amblyopia, diplopia, etherophoria, ecc. Used by the orthoptist, it can be used to measure the angle of strabismus, the heterophorias, the degree of stereopsis, of fusion and convergence and is indispensable for performing ocular motility rehabilitation exercises. The instrument is also able to measure latent strabismus allowing to act promptly in order to correct it before it becomes manifest. It is a device equipped with two eyepieces through which the patient sees two plates with figurines and knobs by means of which the images seen can be moved by making them move away or closer, thus exercising the eye muscles.. It is a non-invasive examination, lasting a few minutes that does not require the instillation of drops and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
HESS-LANCASTER SCREEN
The screen of Hess-Lancaster o test di Hess-Lancaster is an ophthalmological diagnostic test that allows you to diagnose and document any defects in ocular motility, responsible for diplopia, strabismus or paralysis of the eye muscles. The test consists in evaluating the motor coordination of the two eyes and their possible deviation in the various gaze positions, managing to define which ocular muscle is responsible for the deviation. During the exam, the patient is asked to sit in front of a squared screen and wear a pair of glasses with one red and one green lens. Finally, he is given a green torch with which he will illuminate the aim projected by the orthoptist. During the exam, the orthoptist reports the points illuminated by the patient on the test, from which a graph is obtained that allows you to diagnose the possible presence of defects in ocular motility. It is a non-invasive examination that can be performed on patients of all ages, lasting a few minutes that does not require the instillation of drops and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
STUDY OF THE LACRIMAL FUNCTION
Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out this test and computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks. They are non-invasive tests, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
TBT, wink, tear meniscus
Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out this test and computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks. They are non-invasive tests, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
STUDY OF THE MEIBOMIUM GLANDS
Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out this test and computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks. They are non-invasive tests, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
STUDY OF THE PROGRESSION OF THE AXIAL MYOPY IN CHILDREN (MYAH)
Using Topcon's Myah tool. (Link https://topconmyah.com/), our studio is equipped with, it is possible to carry out in addition to computerized and non-invasive tests for the complete study of the tear film, such as imaging of the meibomian glands, the analytical study of the lacrimal meniscus, the study of the blink frequency and the evaluation of aberrations between blinks, also biometry using low coherence optical interferometry (ie the anteroposterior measurement of the eyeball). Myopia occurs due to excessive anteroposterior elongation of the eyeball (axial myopia). It is estimated that the 50% of the world population, including European regions, become nearsighted by 20501. The MYAH tool in children allows you to monitor the progression of myopia and compare the measurements obtained with the growth curves for axial length using the large data set collected by the Erasmus University (Rotterdam, NL)3. Today integrating this data with the use of a new generation of lenses, both in contact and for glasses, in addition to correcting the myopic refractive defect, a "treatment" can be carried out that can slow down the progression of myopia in the age group from 4 to 16 age. The Rx and Axial Length charts allow you to monitor the progression and monitor the effectiveness of the treatment. MYAH provides this data so you can compare changes over time. It is an exam, non-invasive, drops are not instilled and lasts a few minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
1Holden, BA, Fricke, TR, Wilson, DA et al. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology. 2016; 123:1036–42.
2Mandal, P, Berrow, EJ, Naroo SA, et al. Validity and repeatability of the Aladdin ocular biometer. BJO. December 01, 2015. Available from
3Coordinates incorporated in this Myopia device are the most recent available data and originate from the Myopia Research Group of Erasmus MC, Rotterdam
STUDY OF REFRACTIVE DEFECTS IN THE CHILD come on 0 to 5 years by self-refractometry
Auto-refractometry is a computerized diagnostic test capable of determining the objective evaluation sight defects, like myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. The test performed by the auto refractometer, he is able, in a few seconds and in a non-invasive way, to identify the refractive defect of the eye subjected to the examination with absolute precision. The easy-to-perform exam, non-invasive, for both adults and children, it is carried out with high precision computerized tools. To auto-refractometry at our office, it is associated with the measurement of the axial length using the Myah tool from Topcon (Link https://topconmyah.com/). For children from 0 a 6 age, instead, a computerized self-refractometer is used which allows the acquisition of any visual defects at a distance of over 1 metro, instrument specially designed and built for these little patients. It is a non-invasive examination, drops are instilled for pupillary dilation and lasts for a few seconds. At the end of the evaluation, the little patient can resume his activities without particular precautions or warnings.
COLOR SENSITIVITY TEST (Ishihara tablets)
The perception of colors is a complex phenomenon, still not fully clarified, which is achieved thanks to the cortical processing of information transmitted by particular cells of the retina (cones) which are sensitive to the perception of red, of green and blue. A genetic defect involving the lack of one or more of these specialized cells results in a lack of perception of all colors, condition said achromatospia or only of particular colors said dyschromatopsia (including the color blindness). Furthermore, there may be individuals who are sensitive to all three basic colors (trichromatism), but they are deficient, to varying degrees, of the receptors of one of the three basic colors (dyschromatoanomalies). The tests that study such color alterations are mainly the Ishihara test and the test of Fansworth-Munsell. The first is the evaluation in a series of 38 boards (this “Ishihara tablets”) each of which has many circles of different sizes and colors willing to define a "number" or a "path" that is impossible for people with dyschromatopsia to perceive. The "Tablets of Ishihara" is a quick examination, a few minutes, aimed above all at identifying patients suffering from dyschromatopsia of the red-green axis even if they are able to define the extent of the defects in chromatic sensitivity.
COLOR SENSITIVITY TEST (Fansworth-Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision Test).
The perception of colors is a complex phenomenon, still not fully clarified, which is achieved thanks to the cortical processing of information transmitted by particular cells of the retina (cones) which are sensitive to the perception of red, of green and blue. A genetic defect involving the lack of one or more of these specialized cells results in a lack of perception of all colors, condition said achromatospia or only of particular colors said dyschromatopsia (including the color blindness). Furthermore, there may be individuals who are sensitive to all three basic colors (trichromatism), but they are deficient, to varying degrees, of the receptors of one of the three basic colors (dyschromatoanomalies). The tests that study such color alterations are mainly the Ishihara test and the test of Fansworth-Munsell. For the first read COLOR SENSITIVITY TEST (Ishihara tablets). Il test Farnsworth-Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision, o Munsell Vision Test, is a test that evaluates with greater precision and specificity the presence of an anomaly in the perception of colors. Indeed the patient must order, according to his perception of colors, 100 colored tokens that have miniscule differences between them and that cover all the visual shades described by the Munsell color system. The arrangement of the colored pieces is then processed by a computer which identifies with extreme precision any anomalies in the perception of colors (including color blindness). This examination is particularly important for designers, photographers and colorists, as well as in particular sports that require an accurate chromatic vision. The exam lasts approximately 20 minutes and the diagnosis is reported immediately. Both tests can be performed in our office and afterwards the patient can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
STEREOPSIS TEST (Lang I and II)
The binocular vision, also called stereoscopic vision the stereopsi, it is the ability of the visual system to add up a small part of the visual field that is seen simultaneously by the two eyes and to form a single image. The shape, the breadth and visual acuity, of binocular vision are subjective characteristics influenced by genetics and biology of the eyes, from the morphology of the face (nose, eye position and distance, cheeks, eyebrows, ecc), as well as culture, to the experience and knowledge of the objects observed. The binocular vision depends on the merger which involves the activity of the ocular extrinsic muscles, for the positioning of the visual axes on the object concerned and the psychic ability to train, from two similar retinal images, a single visual representation. The stereo it is the perceptive capacity that allows you to combine the images coming from the two eyes, that due to their different anatomical positioning, have a disparity of vision that is exploited by the brain to obtain information on the depth and spatial position of the targeted object and therefore stereopsis allows the generation of three-dimensional vision. The study through fusion and stereopsis test (Stereo Test Lang I e II) are of paramount importance in the development of vision in children from 2 to 5 years as they give us direct information on the state of collaboration of the two eyes and the cortical processing of the images and to highlight a squint.
AMSLER TEST
Although it is a subjective test (just lose the setting for invalidating the test) and is unable to highlight scotomas (alterations in the visual field) below the 6 ° which is the majority represents an extremely easy exam to use, repeatable at home and sensitive enough if done carefully to determine even small and incipient retinal, as well as to monitor evolution of scotomas preexisting. In carrying out the test AMSLER, the patient has to position the grid at about 30 cm, with correction for near-sighted and if you examine each eye. The test grid is able to evaluate the entire macula. Staring at the black dot in center with a focus (absolutely without moving your eyes from this target reference) with good lighting, You can highlight distortions, irregularities and deformations (metamorfospie) the grid in correspondence with possible alterations retinal macular foveali. For this simple test and a subjective, done with care, can be extremely significant for a pathology of the macular and foveal, ie that area of the retina dedicated to vision sharp. Taking care not to move the eye from the black dot, the squares must be observed, which should always be straight and have no interruptions, areas of confusion or distortion. If these were present, it is advisable to contact your ophthalmologist to deepen the study of the macular area with a visit to the fundus and OCT.
WORTH TEST
The test of 4 Worth's lights is a clinical test that evaluates how captured images are transmitted to the brain. The binocular vision, also called stereoscopic vision the stereopsi, it is the ability of the visual system to add up a small part of the visual field that is seen simultaneously by the two eyes and to form a single image. The shape, the breadth and visual acuity, of binocular vision are subjective characteristics influenced by genetics and biology of the eyes, from the morphology of the face (nose, eye position and distance, cheeks, eyebrows, ecc), as well as culture, to the experience and knowledge of the objects observed. The binocular vision depends on the merger which involves the activity of the ocular extrinsic muscles, for the positioning of the visual axes on the object concerned and the psychic ability to train, from two similar retinal images, a single visual representation. Under normal conditions the visual axes, the imaginary lines that join the object with the fovee, converge on a single point. The brain thus receives the image of an object, from each eye, and unites them in a single image. This ability is called Merger. In the merger we distinguish two aspects: a motor one (indicates the ability to align the eyes in order to maintain sensory fusion) and one sensory, aspects that occur simultaneously. Fusion occurs only if the images sent to the brain come from corresponding points and if they are the same in size and sharpness. The WORTH test is used for the study of fusion. The patient is made to wear a pair of glasses with different colored lenses: one red and one green and made to observe 4 lights of different shape and color. He tests, which can be performed both far and near, allows you to assess the degree of cortical fusion of the patient in the presence of diplopia or suppression of one eye and to evaluate the dominant eye.
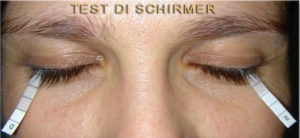
TEST DI SCHIRMER 1 and 2
The Schirmer test proposed in 1903 and now surpassed by computerized tools for the study of the tear film such as the Myah from Topcon (Link https://topconmyah.com/), used in our studio, serves to determine if the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. It is performed with the application of a small strip of graph paper placed between the eye and the eyelid. The test is negative (normal) if the tears absorbed by the paper exceed i 10 mm in 5 minutes or positive (severe hypolacrimia if less than 10 mm, severe hypolacrimia less than i 5 mm). The use of anesthetic eye drops ensures that only the basal tear secretion is measured (Jones test). Secretion varies according to age and other factors (hormonal, width of the eyelid rim, etc..) can affect the sensitivity of the test.
TONOMETRY (Pneumotonometria Goldman)
By tonometry we mean the measurement of eye pressure (tension present inside the eye also called IOP from the Anglo-Saxon acronym Intra Ocular Pressure). This measurement can be performed with the so-called applanation tonometer (Goldmann tonometer considered the "gold standard"), instrument that through contact with the cornea is able to carry out the measurement and in this case a few drops of an anesthetic eye drops and a dye are instilled (fluoresceina) from and alternative, at our studio, the breath tonometer can be used (pneumotonometria) which does not require contact of an instrument with the cornea, therefore the instillation of anesthetic or dye is not necessary and the intraocular pressure measurement is obtained by means of a light puff of air directed towards the patient's eye. Furthermore, this instrument is able to detect the thickness of the cornea (see pachymetry), correcting the measured value with the one actually present inside the eye using an algorithm. Measurement of eye pressure is an indispensable test in the prevention and monitoring of glaucoma, subtle and underestimated disease that can cause irreparable damage to the visual field and sight.
COMPUTERIZED CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY
The corneal topography, also called corneal map, is a test that studies the curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea, in each of its points. The points that have the same curvature are then indicated on the exam printout with the same color, and this print ends up resembling a geographical map with its colored contour lines, that identify, with blue color, for example the sea and its depths, while with the red color the top of a volcano. Corneal topography is of great use, in particular in anticipation of a refractive intervention; it allows the surgeon to know if the cornea has a normal shape, but also to identify irregular astigmatism caused by the imprint on the cornea of excessive use of contact lenses (phenomenon called warpage), keratoconus and other thickness abnormalities. It also allows us to understand if the cornea, for example, has undergone surgery and to highlight any previous trauma or even to study the result of refractive surgery.
VISIT ORTHOPTICS
The orthoptist (or assistant in ophthalmology) is the professional figure who supports the ophthalmologist, in prevention, in the assessment and visual rehabilitation of motor and sensory disturbances of vision. So with the visit orthoptic, the orthoptist is not only able to assess the possible presence of an alteration in the neuromuscular system of the eyes (strabismus, abolition, diplopia, exophoria, esoforia, convergence deficit, etc..), but also to treat these diseases in synergy with the ophthalmologist and often, in small patients, with parents, in order to recover the correct neuro-functional balance of ocular motility and visual function. The orthoptist in fact, in synergy with the ophthalmologist, takes care of the treatment amblyopia or lazy eye, or that condition in which a reduction in visual acuity occurs in one eye (or more rarely of both) determined by a different visual defect between the two eyes, a squint or other alterations of the visual apparatus. It is also useful in the study of patients who are candidates for refractive surgery and those with a high refractive defect in cataract surgery. The orthoptic examination is an examination, non-invasive, drops are not instilled is lasting 20-30 minutes and the patient at the end of the evaluation can resume their activities without particular precautions or warnings.
PEDIATRIC EYE EXAMINATION
The development of vision at birth has only just begun and only during the following ones 6 years will be finished. It is therefore essential, respect a calendar of eye and orthoptic checks that they might highlight a visual problem that the child is unable to perceive or manifest.
So here are the recommended appointments for our children:
1° control. It is carried out in the days following the birth, usually by the pediatrician, with a screening exam (red reflex test) which serves to reveal serious diseases such as retinoblastoma, congenital cataract, congenital glaucoma or other congenital anomalies. Fundus evaluation, carried out by the ophthalmologist, it is also “mandatory” for preterm babies as they could develop retinopathy of the premature baby (ROP).
2° control. Within the first year of life in preterm births, whether or not they develop retinopathy of the premature baby, as the risk of developing visual defects and strabismus in these subjects is greater than in term births. Children of mothers who have contracted must also be checked within the first year of life diseases during pregnancy, such as toxoplasmosis or rubella, children with family members with retinal diseases hereditary and children to whom the pediatrician finds (after 6 months) and'abnormal eye movements or squinting deviations which may or may not be associated with refractive defects.
3° control. Ai 3 years of age, even if the child does not complain of any complaints, a complete eye examination should be performed, essential for identifying refractive and ocular motility abnormalities, diagnose any Amblyopia, (the so-called lazy eye) and undertake the necessary treatment as soon as possible.
4° control. A 5/6 age in conjunction with the start of elementary school. At this age i visual defects they must be corrected promptly to ensure the best possible visual acuity and to better manage their evolution.
5° control. A 8 age because the onset of myopia often occurs at this age, especially if there is a familiarity with this refractive defect.
Subsequently continue with periodic eye exams depending on the information provided by the ophthalmologist.
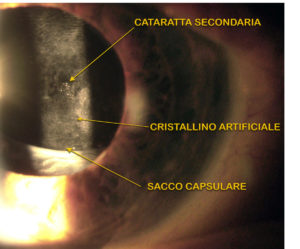
YAG LASER CAPSULOTOMIA
A few months or years after the cataract operation between the 20 and the 30% Of the eyes, the capsule (the outer layer a “bag” of the lens) where the artificial lens is placed, it can become opaque in its posterior part causing a reduction of vision (secondary cataract). This opacity can be permanently removed by laser treatment (capsulotomia YAG laser). Completely painless non-invasive treatment lasting a few minutes that requires only the instillation of eye drops for pupil dilation and possibly anesthetics for the application of a contact lens. At the end of the session, the patient can resume his activities without particular precautions or warnings.

Appointments with Dr.. Benedetti
393 3300030 give her 9.00 All 10.00
Appointments with Dr. Bartolini
0744 205278 give her 9.00 All 13.00